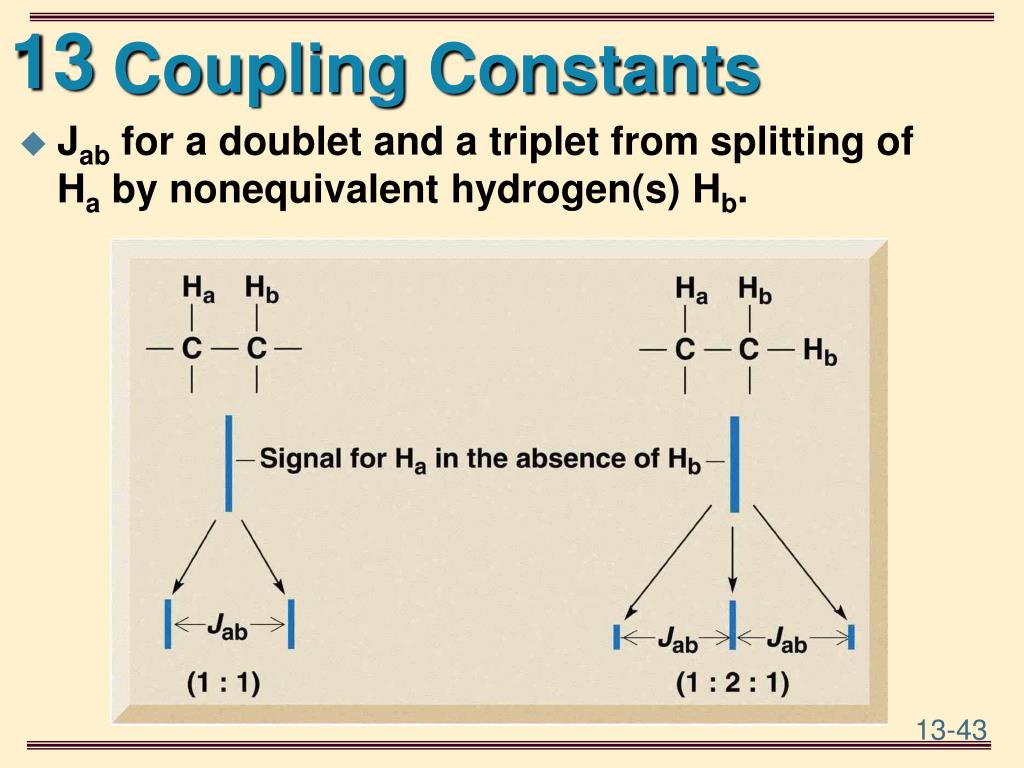
Coupling Constant Hydrogen . thus, coupling constants are. the coupling constant, denoted as j, represents the splitting of nmr signals observed in a spectrum due to the magnetic interactions. when the difference in chemical shift between coupled hydrogen atoms is greater than their coupling constant, the spectrum is said to be. the coupling constant, j (usually in frequency units, hz) is a measure of the interaction between a pair of protons. This constant characterizes the strength of the electromagnetic interaction between elementary charged particles, like electrons and protons. It explains the fine structure splitting of hydrogen atom energy levels, which is how it got its name. The tables below list coupling constants for a few general cases. significance of the fine structure constant. Helpful tool for deciphering complicated aromatic regions, and are especially vital when the chemical shifts ( δ ).
from dxoybmoxg.blob.core.windows.net
Helpful tool for deciphering complicated aromatic regions, and are especially vital when the chemical shifts ( δ ). when the difference in chemical shift between coupled hydrogen atoms is greater than their coupling constant, the spectrum is said to be. This constant characterizes the strength of the electromagnetic interaction between elementary charged particles, like electrons and protons. the coupling constant, denoted as j, represents the splitting of nmr signals observed in a spectrum due to the magnetic interactions. the coupling constant, j (usually in frequency units, hz) is a measure of the interaction between a pair of protons. It explains the fine structure splitting of hydrogen atom energy levels, which is how it got its name. thus, coupling constants are. The tables below list coupling constants for a few general cases. significance of the fine structure constant.
How To Calculate Coupling Constant Of Triplet at Joan Clark blog
Coupling Constant Hydrogen when the difference in chemical shift between coupled hydrogen atoms is greater than their coupling constant, the spectrum is said to be. when the difference in chemical shift between coupled hydrogen atoms is greater than their coupling constant, the spectrum is said to be. the coupling constant, j (usually in frequency units, hz) is a measure of the interaction between a pair of protons. significance of the fine structure constant. the coupling constant, denoted as j, represents the splitting of nmr signals observed in a spectrum due to the magnetic interactions. The tables below list coupling constants for a few general cases. It explains the fine structure splitting of hydrogen atom energy levels, which is how it got its name. This constant characterizes the strength of the electromagnetic interaction between elementary charged particles, like electrons and protons. Helpful tool for deciphering complicated aromatic regions, and are especially vital when the chemical shifts ( δ ). thus, coupling constants are.
From www.researchgate.net
The calculated hyperfine coupling constants of the atoms in P1, P3, and Coupling Constant Hydrogen It explains the fine structure splitting of hydrogen atom energy levels, which is how it got its name. the coupling constant, j (usually in frequency units, hz) is a measure of the interaction between a pair of protons. Helpful tool for deciphering complicated aromatic regions, and are especially vital when the chemical shifts ( δ ). This constant characterizes. Coupling Constant Hydrogen.
From www.chegg.com
Solved Draw an NMR and give the coupling constant J (in Hz) Coupling Constant Hydrogen It explains the fine structure splitting of hydrogen atom energy levels, which is how it got its name. when the difference in chemical shift between coupled hydrogen atoms is greater than their coupling constant, the spectrum is said to be. This constant characterizes the strength of the electromagnetic interaction between elementary charged particles, like electrons and protons. Helpful tool. Coupling Constant Hydrogen.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Lectures 78 Fine and hyperfine structure of hydrogen PowerPoint Coupling Constant Hydrogen the coupling constant, j (usually in frequency units, hz) is a measure of the interaction between a pair of protons. Helpful tool for deciphering complicated aromatic regions, and are especially vital when the chemical shifts ( δ ). This constant characterizes the strength of the electromagnetic interaction between elementary charged particles, like electrons and protons. thus, coupling constants. Coupling Constant Hydrogen.
From www.researchgate.net
Hydrogen production cost for different HTEnuclear reactor couplings Coupling Constant Hydrogen the coupling constant, j (usually in frequency units, hz) is a measure of the interaction between a pair of protons. It explains the fine structure splitting of hydrogen atom energy levels, which is how it got its name. The tables below list coupling constants for a few general cases. significance of the fine structure constant. thus, coupling. Coupling Constant Hydrogen.
From www.bedaflow.com
Permanent drive couplings for hydrogen applications BEDA Coupling Constant Hydrogen significance of the fine structure constant. thus, coupling constants are. It explains the fine structure splitting of hydrogen atom energy levels, which is how it got its name. the coupling constant, denoted as j, represents the splitting of nmr signals observed in a spectrum due to the magnetic interactions. the coupling constant, j (usually in frequency. Coupling Constant Hydrogen.
From www.anyrgb.com
Jcoupling, coupling Constant, chemical Shift, Simple harmonic motion Coupling Constant Hydrogen the coupling constant, denoted as j, represents the splitting of nmr signals observed in a spectrum due to the magnetic interactions. when the difference in chemical shift between coupled hydrogen atoms is greater than their coupling constant, the spectrum is said to be. Helpful tool for deciphering complicated aromatic regions, and are especially vital when the chemical shifts. Coupling Constant Hydrogen.
From www.researchgate.net
Experimental coupling constants through hydrogen bonds Download Table Coupling Constant Hydrogen It explains the fine structure splitting of hydrogen atom energy levels, which is how it got its name. significance of the fine structure constant. the coupling constant, j (usually in frequency units, hz) is a measure of the interaction between a pair of protons. This constant characterizes the strength of the electromagnetic interaction between elementary charged particles, like. Coupling Constant Hydrogen.
From www.chegg.com
Solved Match the following Rydberg constant for hydrogen Coupling Constant Hydrogen This constant characterizes the strength of the electromagnetic interaction between elementary charged particles, like electrons and protons. thus, coupling constants are. the coupling constant, j (usually in frequency units, hz) is a measure of the interaction between a pair of protons. Helpful tool for deciphering complicated aromatic regions, and are especially vital when the chemical shifts ( δ. Coupling Constant Hydrogen.
From www.youtube.com
what is coupling constant in 1HNMR? coupling Constant nmr Coupling Constant Hydrogen It explains the fine structure splitting of hydrogen atom energy levels, which is how it got its name. when the difference in chemical shift between coupled hydrogen atoms is greater than their coupling constant, the spectrum is said to be. Helpful tool for deciphering complicated aromatic regions, and are especially vital when the chemical shifts ( δ ). The. Coupling Constant Hydrogen.
From www.chegg.com
Solved Two adjacent axial hydrogens in a sixmembered ring Coupling Constant Hydrogen It explains the fine structure splitting of hydrogen atom energy levels, which is how it got its name. Helpful tool for deciphering complicated aromatic regions, and are especially vital when the chemical shifts ( δ ). the coupling constant, denoted as j, represents the splitting of nmr signals observed in a spectrum due to the magnetic interactions. thus,. Coupling Constant Hydrogen.
From www.chegg.com
1. Hydrogen Fine structure We showed in class that Coupling Constant Hydrogen thus, coupling constants are. The tables below list coupling constants for a few general cases. the coupling constant, denoted as j, represents the splitting of nmr signals observed in a spectrum due to the magnetic interactions. when the difference in chemical shift between coupled hydrogen atoms is greater than their coupling constant, the spectrum is said to. Coupling Constant Hydrogen.
From ayishaharriet.blogspot.com
Chemistry Chapter 2 Review Measurements And Calculations Answer Key Coupling Constant Hydrogen It explains the fine structure splitting of hydrogen atom energy levels, which is how it got its name. the coupling constant, denoted as j, represents the splitting of nmr signals observed in a spectrum due to the magnetic interactions. The tables below list coupling constants for a few general cases. when the difference in chemical shift between coupled. Coupling Constant Hydrogen.
From www.researchgate.net
Values of couplings constants across the hydrogen bond [Hz] Download Coupling Constant Hydrogen the coupling constant, denoted as j, represents the splitting of nmr signals observed in a spectrum due to the magnetic interactions. the coupling constant, j (usually in frequency units, hz) is a measure of the interaction between a pair of protons. thus, coupling constants are. The tables below list coupling constants for a few general cases. . Coupling Constant Hydrogen.
From www.researchgate.net
1 H NMR coupling for protons 2Ha, 2Hb, and 4H with 3H as evidence Coupling Constant Hydrogen the coupling constant, j (usually in frequency units, hz) is a measure of the interaction between a pair of protons. This constant characterizes the strength of the electromagnetic interaction between elementary charged particles, like electrons and protons. significance of the fine structure constant. when the difference in chemical shift between coupled hydrogen atoms is greater than their. Coupling Constant Hydrogen.
From www.hqhp-en.com
High Quality Hydrogen Dispenser Breakaway Coupling Factory and Coupling Constant Hydrogen thus, coupling constants are. significance of the fine structure constant. the coupling constant, denoted as j, represents the splitting of nmr signals observed in a spectrum due to the magnetic interactions. It explains the fine structure splitting of hydrogen atom energy levels, which is how it got its name. the coupling constant, j (usually in frequency. Coupling Constant Hydrogen.
From dxoybmoxg.blob.core.windows.net
How To Calculate Coupling Constant Of Triplet at Joan Clark blog Coupling Constant Hydrogen Helpful tool for deciphering complicated aromatic regions, and are especially vital when the chemical shifts ( δ ). This constant characterizes the strength of the electromagnetic interaction between elementary charged particles, like electrons and protons. thus, coupling constants are. the coupling constant, j (usually in frequency units, hz) is a measure of the interaction between a pair of. Coupling Constant Hydrogen.
From www.researchgate.net
The nitrogen hyperfine coupling constant, , and correlation time, τ C Coupling Constant Hydrogen thus, coupling constants are. the coupling constant, denoted as j, represents the splitting of nmr signals observed in a spectrum due to the magnetic interactions. significance of the fine structure constant. It explains the fine structure splitting of hydrogen atom energy levels, which is how it got its name. This constant characterizes the strength of the electromagnetic. Coupling Constant Hydrogen.
From www.researchgate.net
Strong coupling constant as a function of the energy. Download Coupling Constant Hydrogen This constant characterizes the strength of the electromagnetic interaction between elementary charged particles, like electrons and protons. when the difference in chemical shift between coupled hydrogen atoms is greater than their coupling constant, the spectrum is said to be. The tables below list coupling constants for a few general cases. the coupling constant, denoted as j, represents the. Coupling Constant Hydrogen.